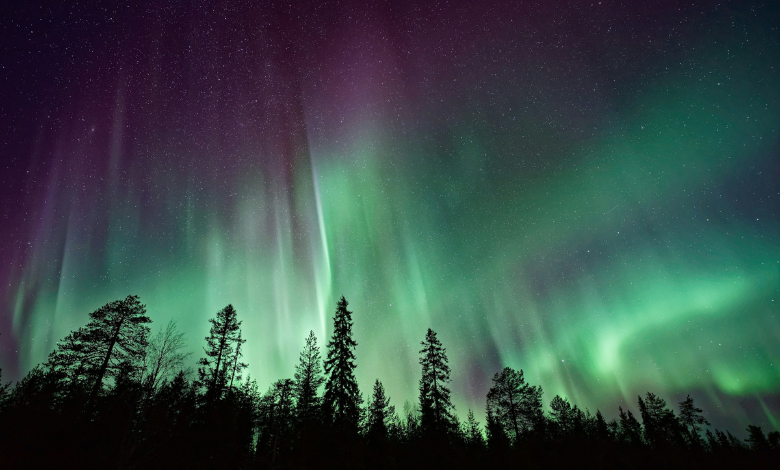
Illuminating the Skies: Exploring the Climate Connections of Northern Lights in North America

Introduction: Unveiling Auroras
In the vast expanse of the night sky, an entrancing phenomenon has been enthralling both scientists and sky watchers: the mesmerising display of auroras. Recently, the breathtaking spectacle of auroras painting the northern skies of North America has been causing a significant buzz across news headlines and social media. But beyond their enchanting beauty, these otherworldly lights offer a deep understanding of our planet’s climate dynamics.
Solar Storms: Celestial Stimuli
Essence of this celestial performance are solar storms, powerful eruptions from the Sun that hurl charged particles towards the Earth. When these particles converge with our atmosphere, they kindle a luminous display known as auroras. While solar storms have been an elemental event for centuries, their impact on Earth’s climate is accumulating increasing eyeballs and attention.
Geomagnetic Disruption: Impact on Tech
One critical aspect of this occurrence is its relationship with Earth’s magnetic field. Solar storms can interrupt this protective shield, leading to geomagnetic storms. These storms in turn, can disrupt satellite operations, intervene the communication system, and even pose risks to power grids.
Such perturbations highlight the complicated connection between our technological infrastructure and celestial events.
Climate Dynamic: Solar- Aurora Interaction
However, the climate ramifications of auroras extend beyond their immediate influence on technology. Recent research suggests a more intricate relationship between Earth’s climate patterns and solar activity. Solar storms, while transient disruptions, may sway atmospheric circulation, modifying weather patterns on a regional scale.
Historical Insight: Aurora’s Climate Signs
Moreover, the frequency and severity of auroras may offer perceptions about long term climate trends. Changes in solar activities over epochs have been associated with oscillations in Earth’s climate, which includes the period of cooling and warming. By scrutinising historical records of auroral activity, scientists can recreate past climate variations, providing valuable insights into Earth’s climatic history.
Upper Atmosphere: Climate Modelling Key
Moreover, the study of auroras contributes to our understanding of the upper atmosphere, a key aspect of Earth’s climate system. The interaction between the upper atmosphere and solar particles can instigate chemical reactions that influence the distribution of ozone and other greenhouse gases. Understanding these procedures is essential for precise climate modelling and anticipating future climate trends.
Cultural Importance: Indigenous Mythology
In addition to their scientific relevance, auroras hold the spiritual and cultural importance of aboriginal communities across North America. For generations, these awe- inspiring manifestations have been woven into the compositions of indigenous mythology and traditions, symbolising the intertwining of all living beings with the cosmos.
As we marvel at the steller exhibition of auroras painting the northern skies, it’s vital to acknowledge the broader ramifications of these phenomena. From their cultural significance to their role in shaping Earth’s climate, auroras offer a glimpse into the complicated structure of interactions that govern our planet and the universe beyond. By researching and appreciating these phenomena, we deepen our grasp of the fragile balance that upholds life on Earth and the infinite wonders of the cosmos.