Explore top 10 facts about Plumas National Forest

Tucked up in California’s northern Sierra Nevada mountains, Plumas National Forest is a stunningly beautiful and biologically diverse area. This forest, which covers an area of more than 1.1 million acres, gives visitors the chance to discover a variety of ecosystems, beautiful scenery, and recreational activities. The top 10 facts about Plumas National Forest are shown below.
1. Establishment

The name Plumas National Forest, which was adopted on July 1, 1905, comes from the Spanish term meaning “feathers,” which reflects the rich foliage of the many conifers in the region that resembles feathers.
2. Location
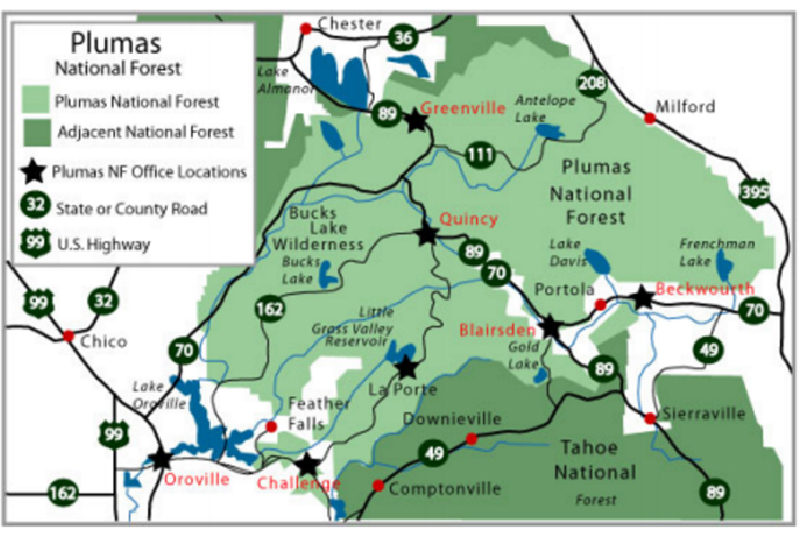
Plumas National Forest is located in northeastern California and is spanned across Plumas, Butte, Sierra, and Lassen counties. It is situated about 60 miles to the north of Sacramento, the state capital.
3. Ecological Diversity

Numerous habitats, such as montane forests, meadows, lakes, rivers, and alpine peaks, may be found within Plumas National Forest. Numerous species of animals, such as bald eagles, black bears, mule deer, and the endangered Sierra Nevada red fox, find home in the forest.
4. Recreational Opportunities
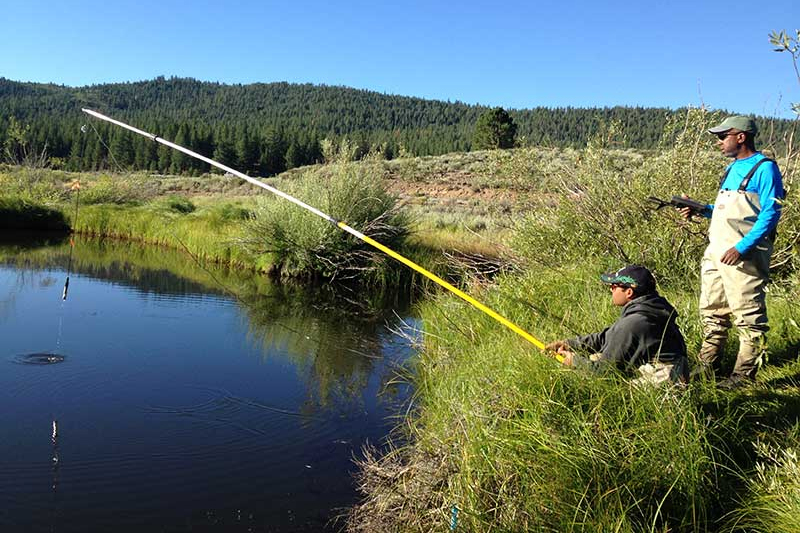

Numerous recreational pursuits are available to visitors to Plumas National Forest, such as hiking, camping, fishing, boating, mountain biking, and animal observation. There is plenty for outdoor enthusiasts of all ages in the forest, which is home to several campgrounds, hiking trails, and picturesque views.
5. Feather River
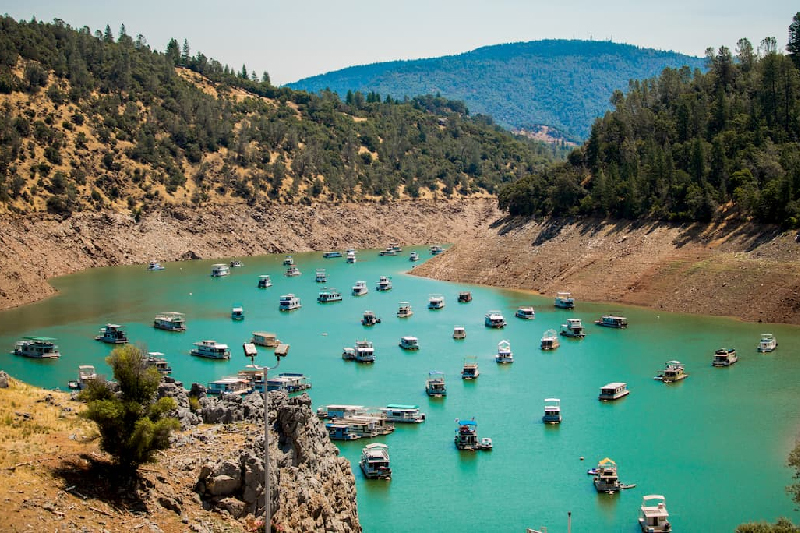

Plumas National Forest is traversed by the Feather River, one of California’s principal streams. In addition to offering chances for fishing, kayaking, and rafting, the river serves as an essential habitat for fish species including salmon and trout.
6. Historic Sites

Plumas National Forest is rich in history, with numerous historic sites and landmarks scattered throughout the forest. These include old mining towns, Native American archaeological sites, and remnants of the region’s logging and railroad history.
7. Butterfly Valley
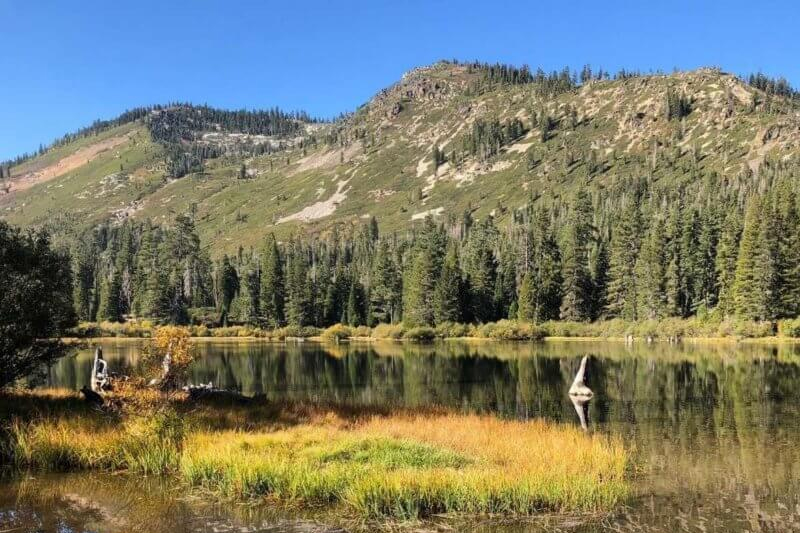

Botanical Area Located within Plumas National Forest, the Butterfly Valley Botanical Area is home to a diverse array of plant species, including rare and endemic plants. Visitors can explore the area via hiking trails that wind through lush meadows and forests.
8. Pacific Crest Trail
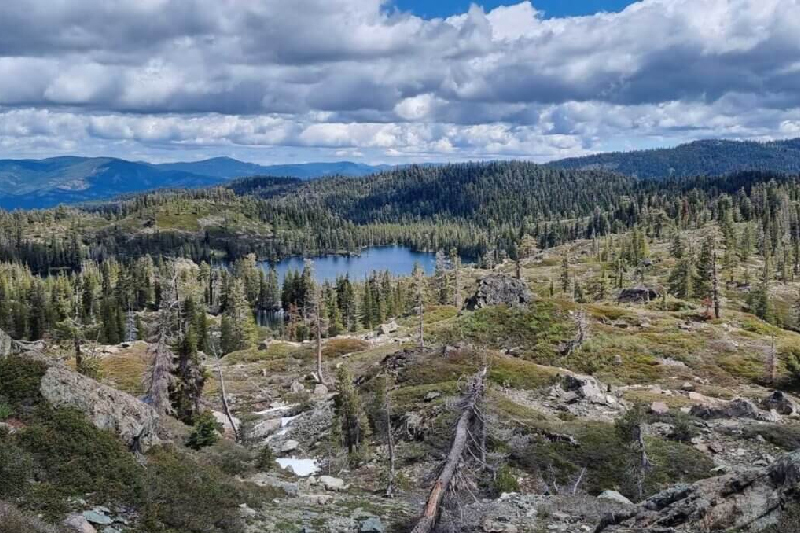

A portion of the famous Pacific Crest Trail traverses through Plumas National Forest, offering hikers the chance to experience stunning mountain scenery and pristine wilderness. The trail provides access to high alpine lakes, towering peaks, and panoramic vistas.
9. Fire Management
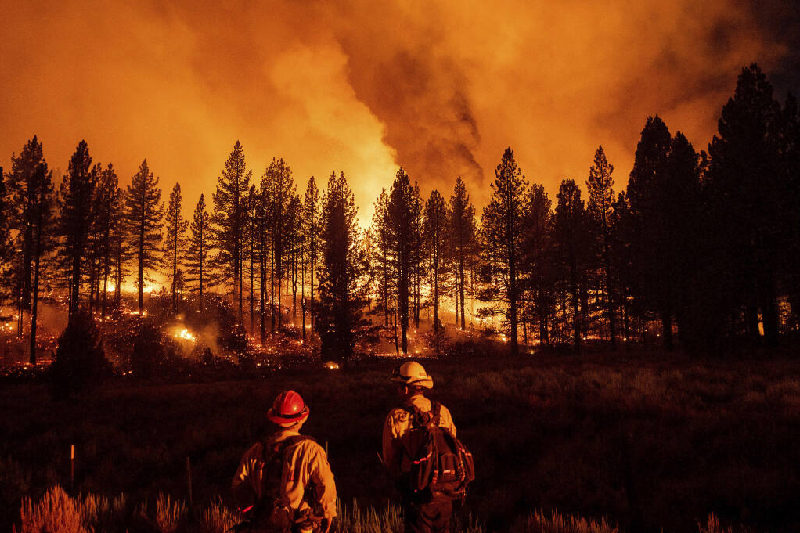

Like many forests in California, Plumas National Forest is susceptible to wildfires. The forest service actively manages fire through prescribed burns, fuel reduction projects, and fire suppression efforts to protect communities and ecosystem health.
10. Conservation Efforts
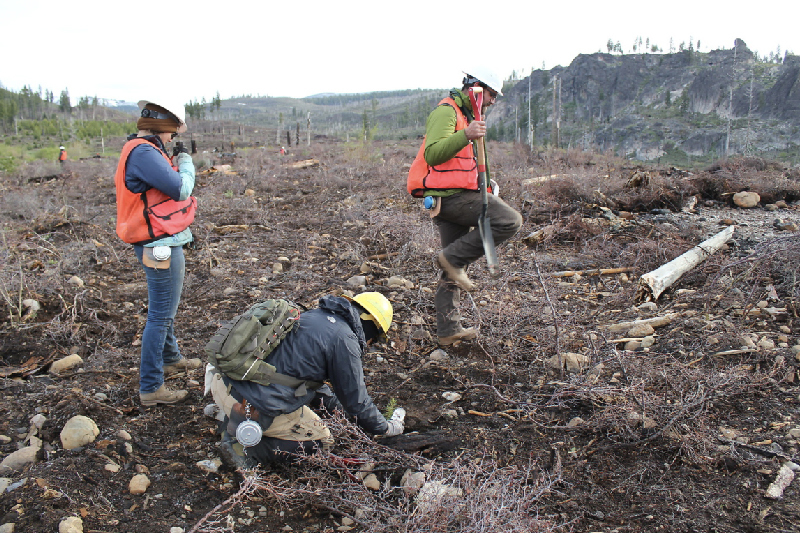

Plumas National Forest is managed by the U.S. Forest Service, which works to balance conservation with sustainable land use practices. Efforts are underway to protect sensitive habitats, restore degraded areas, and promote biodiversity conservation within the forest.
To summarize, Plumas National Forest offers an abundance of scenic views, leisure pursuits, and cultural legacy. This magnificent woodland offers something for everyone, regardless of your desire for outdoor activity or just to spend time in nature. A true jewel of the Sierra Nevada, Plumas National Forest boasts a rich history, a variety of habitats, and ongoing conservation initiatives.


